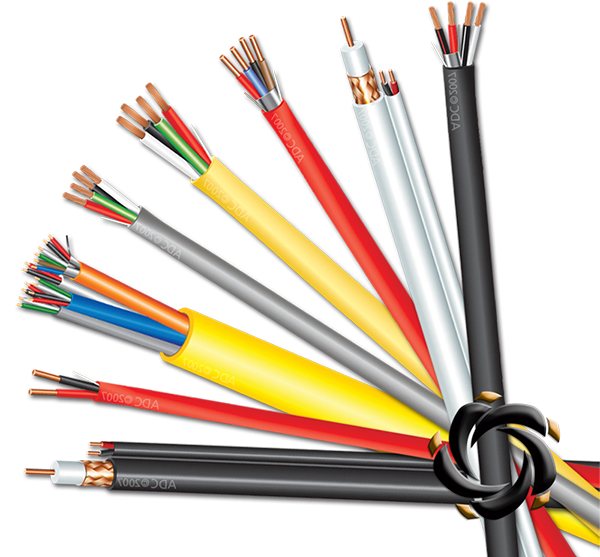
When selecting 50 Ohm Flexible Coaxial Cable for high-power RF applications, the power handling capacity of the cable is a primary factor. Power handling refers to the maximum amount of RF power that the cable can transmit without causing damage to its internal structure or performance degradation. The cable’s inner conductor, dielectric material, and outer shield must be able to withstand the power generated by the system without causing signal loss, overheating, or breakdown. High-power RF signals often generate significant heat, which can lead to voltage breakdown or degradation of the dielectric material. The power rating is generally expressed in watts, and this figure should reflect the peak power and continuous power the system requires. It's crucial to choose a cable with a power rating that exceeds the maximum power anticipated in the application, providing a margin of safety for reliable performance without risking signal distortion or failure.
Attenuation refers to the loss of signal strength as the RF signal travels along the coaxial cable. In high-power RF systems, attenuation can have a significant impact on system performance, especially over long distances. Signal loss typically increases with the frequency of the RF signal and the length of the cable. For high-power RF applications, it is essential to select a cable with low attenuation characteristics to ensure minimal signal degradation. The attenuation is influenced by the material of the inner conductor (such as copper or silver-plated copper), the dielectric material (like foamed PTFE or polyethylene), and the cable’s overall construction. Foamed dielectric cables tend to offer lower attenuation than solid dielectric cables because they have less material, which reduces signal loss. The length of the cable also plays a significant role—longer cables experience greater attenuation. For high-power RF systems, maintaining low attenuation is crucial to ensure signal integrity and consistent performance across the transmission distance.
The dielectric material of a coaxial cable separates the inner conductor from the outer shield and plays a critical role in determining the cable's overall performance and safety under high-power conditions. Dielectric materials must have sufficient dielectric strength to resist breakdown when exposed to high voltage levels. The dielectric strength is defined as the maximum voltage the material can withstand without electrical breakdown. High-power RF applications can result in significant voltage spikes that could exceed the dielectric's capacity, especially if the cable is improperly sized or has lower-grade dielectric material. Materials like PTFE (Teflon) and foam polyethylene are often used for high-power RF applications because they offer high dielectric strength, low loss, and thermal stability. The choice of dielectric material also affects the capacitance of the cable, which can influence both the signal quality and the power handling. For high-power systems, selecting a dielectric material that balances dielectric strength and attenuation is crucial for maintaining system performance under extreme electrical conditions.
Alongside power handling, the voltage rating of a coaxial cable is essential in high-power RF applications. The voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage that the cable can handle without causing failure or degradation of the dielectric material. High-power RF signals can cause voltage surges that may exceed the dielectric's breakdown threshold, leading to arcing or insulation failure. It’s essential to select a cable with a voltage rating that aligns with the maximum operating conditions of the system. If the RF signal includes pulses or if the system involves high peak voltages, the cable must be able to handle these transient conditions without compromising signal quality. For instance, if your application involves high-voltage RF signals such as those in radar systems or microwave communications, selecting a cable rated for higher voltages ensures safety and reliability in the long term. A mismatch between the voltage rating and the system’s operating conditions could lead to breakdown of the cable's insulation, resulting in signal loss or system damage.
Shielding is one of the most important features when selecting 50 Ohm Flexible Coaxial Cables for high-power RF signals, especially in environments where electromagnetic interference (EMI) is a concern. Shielding prevents external signals from contaminating the transmitted signal and also reduces the risk of signal leakage. For high-power RF systems, the cable must have adequate shielding to maintain signal integrity and prevent the generation of harmonics or other unwanted emissions that can interfere with nearby electronics. Common shielding types include braided shields, foil shields, or combination shields (braid plus foil). Braided shields are highly effective at preventing radiation leakage at low frequencies, while foil shields provide excellent protection at higher frequencies. The choice of shielding depends on the level of protection required for the application. For instance, double-shielded cables (braid and foil) are typically preferred for environments with high levels of external electromagnetic interference. Proper shielding ensures that the RF system operates without interference and minimizes potential signal degradation from external sources.