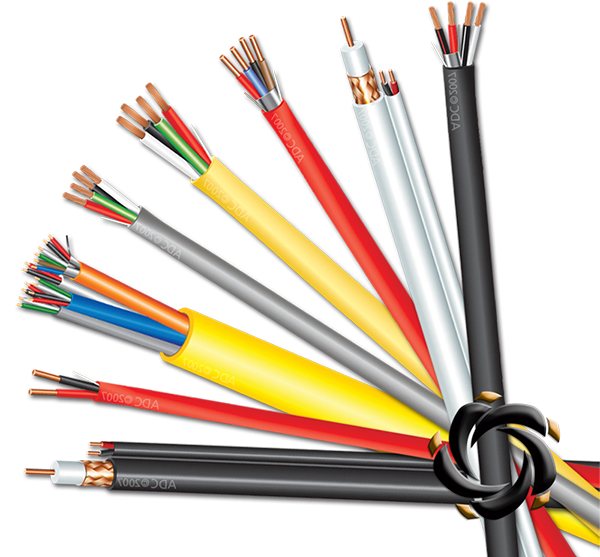
High-Temperature Resistance
The insulation material of the Fire Resistant Alarm Cable is specifically chosen for its ability to withstand extreme temperatures without compromising its structural integrity. Materials such as ceramic-based compounds, silicone rubber, mineral-filled PVC, and low-smoke halogen-free polymers are commonly used in the construction of this type of cable. These materials have exceptional heat resistance and can endure sustained high temperatures typically encountered in fire scenarios, often reaching up to 105°C or more. By maintaining its insulating properties under intense heat, the cable ensures that the electrical components inside, such as the conductors, are protected from thermal degradation, preventing the risk of short circuits or signal loss. The heat resistance also ensures that the cable will not melt or break down under fire conditions, allowing the alarm system to continue operating for a critical period, even as temperatures rise.
Flame Retardant Properties
In addition to heat resistance, the insulation of the Fire Resistant Alarm Cable is treated with flame-retardant materials designed to prevent the cable itself from igniting or burning in the event of a fire. These flame-retardants either function by chemically altering the combustion process, delaying ignition, or by forming a protective char layer over the surface of the insulation when exposed to flames. This charred layer acts as a barrier to prevent further spread of the flame. These flame-retardant properties are essential in ensuring that the cable does not become a source of ignition or contribute to the escalation of a fire. The materials used often meet stringent fire safety standards and are tested to ensure that they perform effectively during real-world fire scenarios. The ability of the insulation to suppress flames also enhances the overall fire safety of the building by reducing the chances of the fire spreading along the cable.
Maintaining Electrical Continuity Under Heat Stress
One of the most important functions of the Fire Resistant Alarm Cable’s insulation is its ability to maintain electrical continuity even when subjected to heat. Alarm systems rely on a steady flow of electrical signals to function correctly, and during fire, this becomes even more critical. The insulation is designed to protect the conductors from the intense heat, preventing them from melting or short-circuiting. The cable ensures that the electrical signals continue to flow uninterrupted for a set period, which is critical for maintaining alarm system functionality during the initial stages of a fire, when evacuation or emergency actions are most crucial. The insulation’s resilience under heat stress is a key factor in ensuring that the alarm system remains fully operational, even when exposed to flames or high temperatures.
Thermal Stability and Low Smoke Emission
Many Fire Resistant Alarm Cables feature low-smoke, zero-halogen (LSZH) insulation, which is engineered not only to resist high temperatures but also to produce minimal smoke when exposed to fire. The importance of low smoke production in fire-resistant cables cannot be overstated. In the event of a fire, minimizing the amount of smoke generated by the cable reduces the risk of toxic smoke inhalation and ensures that the escape routes remain safer for people evacuating the building. LSZH materials are free from halogens, which are known to emit toxic gases when burned, ensuring that the cable does not contribute to the toxicity of the environment during a fire. Additionally, the reduced smoke emission allows for better visibility, improving the chances of successful evacuation and emergency response.
Prevention of Insulation Degradation
Over time, exposure to high temperatures can cause the insulation of standard cables to degrade, leading to cracking, brittleness, or complete failure of the material. In contrast, the insulation of the Fire Resistant Alarm Cable is specifically designed for long-term thermal stability. It is made from materials that do not degrade quickly even when exposed to heat for extended periods. This ensures that the cable continues to protect the conductors and maintain its structural integrity, even in high-temperature environments over time. The insulation is engineered to resist thermal aging, meaning that it will not crack or become brittle after prolonged exposure to heat. This characteristic is particularly crucial in environments where the cable is exposed to fluctuating or elevated temperatures over the lifespan of the system.