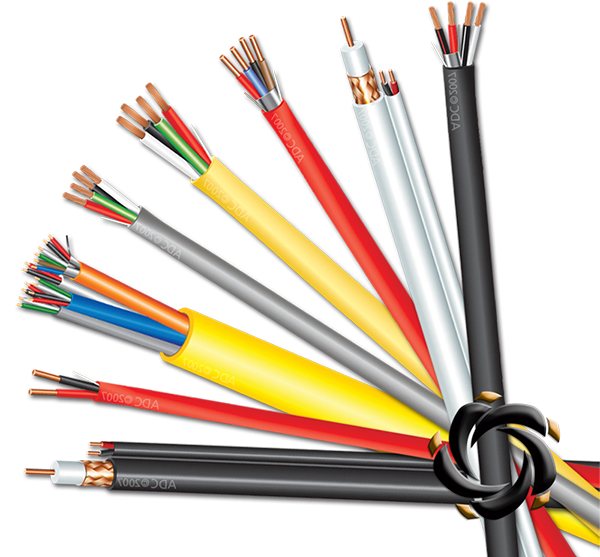
1. Data Transmission Speed (Bandwidth)
When selecting telecommunication cables, the data transmission speed, or bandwidth, plays a pivotal role in ensuring that the network can handle the expected traffic. Fiber-optic cables are designed to deliver ultra-high-speed data transfers, often supporting bandwidths of up to 100 Gbps and beyond, making them the ideal choice for large-scale, high-demand networks such as data centers, backbone networks, and 5G infrastructure. On the other hand, copper cables, such as Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a, support more modest bandwidths, ranging from 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps, and are better suited for local networks, office setups, or home installations. The speed requirements of the network, along with the nature of the data being transferred (e.g., high-definition video, large data files, or routine office communications), should guide the decision between copper and fiber-optic solutions.
For high-speed data transmission, especially in areas like video conferencing, cloud applications, or high-definition media streaming, choosing cables with higher bandwidth, like fiber-optic, ensures that the network can deliver the required performance without bottlenecks, ensuring a seamless user experience.
2. Distance (Signal Attenuation)
The distance between devices in a network is another important factor when selecting the correct telecommunication cables. As the signal travels through the cable, it undergoes attenuation, where the signal strength weakens. Fiber-optic cables are highly advantageous in this regard, as they offer minimal signal loss over long distances, allowing data to be transmitted over several kilometers without significant degradation. This makes fiber-optic cables ideal for applications requiring long-distance connections, such as inter-building connections or undersea cables for international communication networks. Copper cables, particularly Cat 5e and Cat 6, are effective for shorter distances, typically up to 100 meters for Gigabit Ethernet. Beyond this range, signal degradation becomes a concern, especially for high-speed data.
For network environments that span large areas, such as campus networks or urban-wide infrastructure, fiber-optic cables offer a reliable, low-latency solution to ensure uninterrupted data transfer, regardless of the distance between devices.
3. Environmental Conditions (Temperature, Humidity, and Interference)
The installation environment is a critical consideration in cable selection, as telecommunication cables must be able to withstand the specific conditions in which they are used. For example, fiber-optic cables are naturally resistant to electromagnetic interference (EMI), making them highly suitable for environments with high electrical noise, such as industrial plants or data centers with dense networking equipment. Moreover, fiber-optic cables are typically weatherproof and capable of withstanding extreme temperatures and outdoor elements, making them ideal for outdoor installations, underground systems, or long-haul communication lines.
On the other hand, copper cables are more susceptible to interference from external sources like motors, power lines, and other devices emitting electrical signals. Therefore, in environments with high EMI, shielded copper cables (e.g., STP, FTP) can help reduce the potential for signal disruption. Additionally, temperature extremes and humidity can also impact copper cables, causing degradation over time. Outdoor-rated cables are necessary for these conditions, which are usually equipped with special insulation and protective coatings to prevent weather-related damage.
4. Cable Type (Fiber vs. Copper)
The decision between fiber-optic cables and copper cables is influenced by the specific performance requirements and budget constraints of the network. Fiber-optic cables are the go-to option for high-performance networks, offering superior data transfer speeds, low attenuation, and resistance to electromagnetic interference. Their ability to transmit data over long distances with minimal signal loss makes them the preferred choice for modern infrastructures like backbone networks, 5G installations, and long-haul telecommunications.
On the other hand, copper cables, such as Cat 5e and Cat 6, remain popular for local area networks (LANs) and short-range communication, where the cost and installation time are significant considerations. Copper cables tend to be more affordable than fiber optics, making them a better fit for budget-sensitive projects that do not require the extensive bandwidth or long-distance capabilities of fiber.
5. Power Over Ethernet (PoE) Requirements
For Power over Ethernet (PoE) applications, where both data and electrical power are transmitted through the same cable to power devices such as IP cameras, VoIP phones, and wireless access points, the selection of the correct cable is crucial. Copper cables, particularly Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a, are commonly used for PoE installations, as they are designed to support both the data and power needs of devices. Higher categories, such as Cat 6a, offer greater power transmission capabilities and can handle the higher current demands of devices that require more power, such as Pan-Tilt-Zoom cameras or heating systems.
Fiber-optic cables, while excellent for high-speed data transmission, are not suited for PoE applications since they cannot carry electrical power along with the data. Therefore, for installations requiring PoE, copper-based cables are the preferred option.
6. Cost and Budget Constraints
The selection of telecommunication cables is also significantly influenced by cost considerations. While fiber-optic cables offer superior performance, they are typically more expensive than copper cables in terms of both material cost and installation. Installing fiber-optic cables requires specialized tools and skilled technicians for fusion splicing and termination, which can increase the installation cost.
In contrast, copper cables are generally less expensive and are easier to install with standard tools. For smaller-scale installations or home networking systems, copper cables (such as Cat 5e or Cat 6) can provide an affordable and effective solution, especially for networks with less demanding speed and distance requirements. However, for high-speed, long-distance, or high-capacity networks, investing in fiber-optic cables is a more future-proof solution, despite the higher upfront costs.