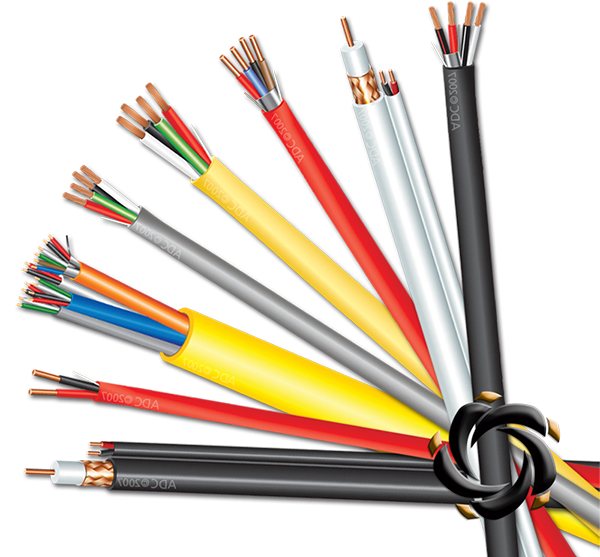
Shielding as a Barrier Against Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
-
Preventing External Interference: In today’s technology-driven environments, electromagnetic interference (EMI) is an ever-present challenge. EMI arises from various sources such as electrical devices, power lines, radio waves, and even wireless communication. This interference can degrade the quality of the signal, introducing unwanted noise or distortion. The shielding in 75 Ohm Coaxial Cable acts as a robust electromagnetic barrier, blocking these external signals from entering the cable and disrupting the transmission of the intended signal. This shielding is particularly crucial in sensitive applications like television broadcasting, networking, and data centers, where signal clarity and integrity are paramount.
-
Reducing Radio Frequency Interference (RFI): Radio Frequency Interference (RFI), often caused by nearby transmitters, can degrade high-frequency signals. The shielding in 75 Ohm Coaxial Cable blocks these high-frequency radio signals from affecting the cable’s internal transmission. With a well-designed shield, such as braided or foil shielding, the cable effectively prevents external radio signals from infiltrating the system, ensuring that the transmitted signal remains unperturbed by surrounding wireless signals or broadcast frequencies.
-
Prevention of Signal Cross-Talk: In installations where multiple cables are laid side-by-side, such as in a network rack or broadcasting environment, cross-talk—the interference caused by signals from adjacent cables—can be an issue. Shielding in 75 Ohm Coaxial Cable helps to isolate each cable and minimize cross-talk, ensuring that signals in one cable do not leak into adjacent cables, which could lead to signal distortion or data loss.
Types of Shielding in 75 Ohm Coaxial Cable
-
Foil Shielding: Foil shielding, usually made from aluminum or copper, provides a thin, continuous barrier around the cable’s dielectric layer. This shielding is especially effective at blocking high-frequency interference, such as that caused by radio signals or electromagnetic pulses. Since the foil is very thin and covers the entire surface of the dielectric, it offers 100% coverage, which is ideal for blocking small and high-frequency noise. Foil shields are often found in video transmission systems or data cables, where high-frequency stability is critical.
-
Braided Shielding: Braided shielding involves a mesh of thin metal wires, typically copper or aluminum, that is woven into a dense layer around the dielectric core. The braided shield provides mechanical strength and offers excellent protection against low- to medium-frequency interference. It also allows the cable to be more flexible, which is crucial in environments where the cable may be frequently moved or bent. Braided shielding provides more protection than foil shielding when it comes to physical durability and is less susceptible to damage during installation or use.
-
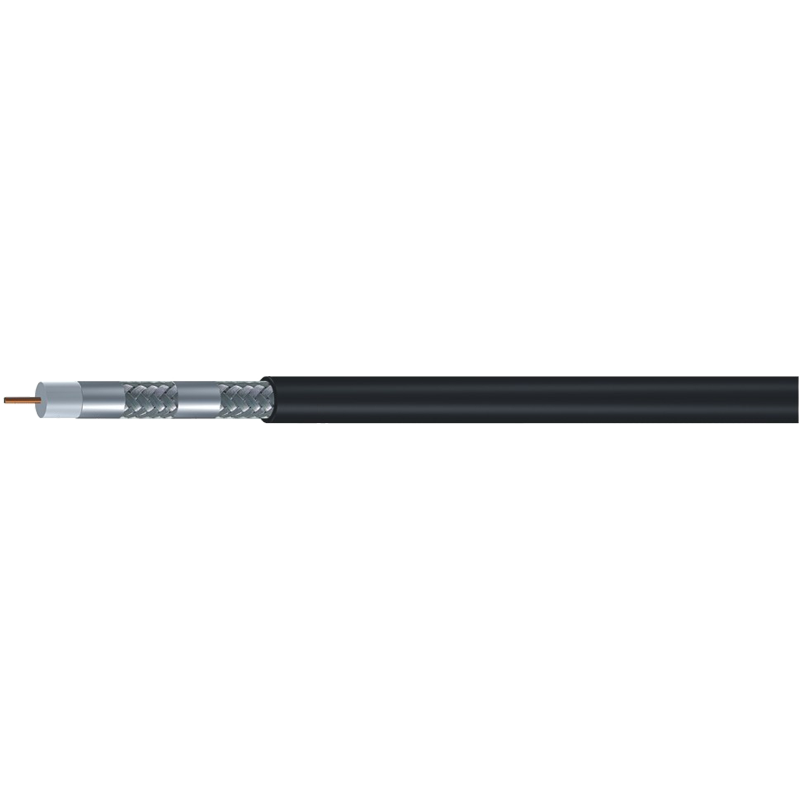
Combination of Foil and Braided Shields: Some 75 Ohm Coaxial Cables combine both foil and braided shielding, offering the best of both worlds. This dual-layer shielding enhances both high-frequency protection and mechanical robustness. It ensures that the cable is well-protected from both external interference and physical stress, making it suitable for high-performance data applications, including video surveillance systems, broadcasting, and telecommunications.
Prevents Signal Leakage
-
Containing the Transmitted Signal: One of the key functions of the shielding is to contain the transmitted signal within the cable. A poorly shielded coaxial cable will allow the signal to leak out, especially at higher frequencies. This leakage results in signal degradation and can cause interference with nearby devices. 75 Ohm Coaxial Cable with robust shielding ensures that the signal is confined within the cable, preserving the signal strength and quality over long distances.
-
Minimizing Attenuation: Attenuation, or signal loss, is a significant concern in long-distance signal transmission. Without effective shielding, signals can weaken as they travel along the cable, leading to loss of clarity and detail. The shielding not only prevents external signals from entering but also minimizes the internal signal loss by containing the energy, ensuring that the signal remains stronger and travels farther without degradation.
-
Signal Integrity Over Distance: For high-frequency applications such as HD video transmission or fiber optic cable replacements, even small amounts of signal loss can lead to noticeable degradation. The shielding helps maintain signal integrity by preventing leakage and preserving the strength of the signal, ensuring that the transmission quality remains stable, even over longer cable runs.